[ad_1]
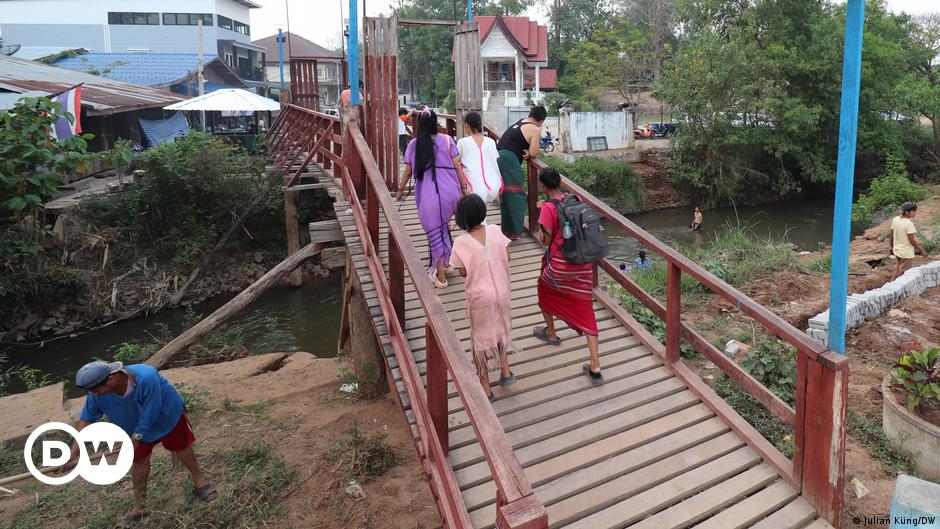
In the village of Wale, Thailand and Myanmar are connected by a small wooden bridge. The narrow river that flows beneath it constitutes the border. The villages on the two banks share the same name, and their lives are closely entwined. Locals carry rice and vegetables back and forth across the little footbridge; children splash and play in the water below. The Thai border guard in the observation post is paying far more attention to his cellphone than to the flow of commuters.
The majority of people who cross here are from the local villages. In recent weeks, however, an unusually large number of young people from other parts of Myanmar have been crossing the border in this quiet village.
“I can spot them straight away by their big rucksacks,” said Tungsa, as she plays dominoes outside her general store on the Myanmar side of the river.
‘If they make it here, they’re safe’
These young people are fleeing conscription into Myanmar’s military. Thousands are seeking to go abroad before mandatory military service comes into effect in April, for men between 18 and 35 years old and women aged 18 to 27. Anyone who doesn’t go into hiding risks being ordered, as a soldier, to commit war crimes. And refusing to do military service is punishable by several years in jail.
“If they make it here, they’re safe,” said Tungsa. That’s because the Myanmar side of Wale is controlled by the Karen National Union. It’s one of the ethnic militias that are fighting the Myanmar army inside the country on several fronts. The military junta has suffered some bitter defeats in recent months.
The United States Institute of Peace estimates that the Myanmar army has just 130,000 soldiers at most, and that only about half are combat-ready. Observers believe the impending obligatory conscription is a desperate attempt to forcibly augment their greatly reduced troop numbers. And so more and more young people trying to escape conscription are now thronging into neighboring Thailand.
In the past few weeks, hundreds have been arrested by patrolling border police. Human rights activists report that, depending on the policeman or arresting authority, they may be detained, sent back over the border, or, on occasion, released on payment of a bribe.
Porous ‘green border’ allows many to cross
However, most refugees from Myanmar make it into Thailand undetected, either by sneaking across the porous, virtually unguarded jungle border, or by mingling with regular commuters. At the Ban Mun Ru Chai river border to the west of Wale, the Thai guard post isn’t even staffed. A couple of goats who have taken up residence watch the many people crossing the river to the Thai side.
The Thai government seems to have been wholly unprepared for the situation in Myanmar, said security expert Panitan Wattanayagorn, a professor at Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok. He assumes that fighting between the military junta and resistance groups will intensify over the coming months, and that forced conscription will continue to drive people across the border into Thailand. On the TV channel Thai PBS, Wattanayagorn warned that Bangkok urgently needs to put measures in place to deal with the impending influx of refugees from Myanmar.
The Thai foreign minister has announced plans to establish a humanitarian security zone along the western border, providing refugees with food and medical assistance. However, authorities have not given any information about where exactly the protected zone would be located, or when it would be established.
Meanwhile, only random checks are being carried out along the 2,000-kilometer (1,240-mile) border between Myanmar and Thailand. “I check people on a random basis,” said the border guard in Wale. Last week, he arrested six people trying to escape conscription. But “sometimes I just let them through,” he admited, fixing his attention on his plate of rice as three people from Myanmar scuttled unchallenged over the bridge.
Thailand needs cheap workers from Myanmar
People in Wale don’t seem to fear an influx of refugees. “Just let them all in,” said Pattanew, a motorcycle taxi driver who is at the waiting area near the border bridge. He transports day laborers on the back of his moped; they work for very little money, tending Thai fields and cleaning houses. “Without the migrant workers from Myanmar, we would have a lot of issues,” he said. “They’re very hardworking; they tolerate the sun and rain and don’t complain.”
Most of his passengers work in the surrounding border region. The new refugees, on the other hand, mostly travel on to big cities like Bangkok, Chiang Mai or the migrant quarter of Samut Sakhon, where they find places to stay among their fellow countrymen.
It’s estimated there are between 2 and 3 million people from Myanmar living in Thailand. No one knows the exact number, as many are in the country illegally. One of them, a man in his early 20s, asked to be referred to by the pseudonym “Mao Uh.” He’s afraid that otherwise, he may be detected by the authorities’ radar.
Hoping for a work permit
It has been almost a month since he left his family in Ayeyarwady, west of Yangon, and set out for Thailand. The journey was a nerve-wracking one. Every time he passed through one of the junta’s checkpoints, he ran the risk of being detected and arrested. “I was very lucky,” he said. Eventually he made it across the “green border” in the countryside, into Thailand.
Since then, he has been holed up in a Bangkok suburb, in a stuffy room that he seldom leaves. He’s worried about his sister back home. Like him, she faces being called up for military service.
“We’ve already agreed that she’ll follow as soon as I have work here,” said Mao. Ideally, he would like to work in the security sector as a guard, protecting people. But essentially he’s prepared to do any work, “no matter what, no matter where.”
Mao is hoping for a so-called worker amnesty from the Thai authorities. Four times a year, illegal migrants can apply for an amnesty that will allow them to work in the country legally for a certain period of time. However, labor lawyers are critical of the procedure; they say it’s too complicated and susceptible to corruption, which is why many refugees from Myanmar simply work illegally.
Thai authorities ‘turning a blind eye’
According to the International Labor Organization, the invisible migrant workers from Myanmar already contribute up to 6.6% of Thailand’s GDP. Sompong Srakaew from the Labor Rights Promotion Network is convinced the influx of workers from the neighboring country will further support the economy. “It’s good for the Thai economy, because employers need cheap workers to remain competitive,” he said.
Srakaew, who advocates for migrant rights, estimates more than 10,000 people fleeing conscription have already crossed the border, with more coming every day. “It seems that the Thai authorities are turning a blind eye, and allowing many to enter the country unofficially,” he said.
This article was originally written in German.
[ad_2]
Source link