[ad_1]
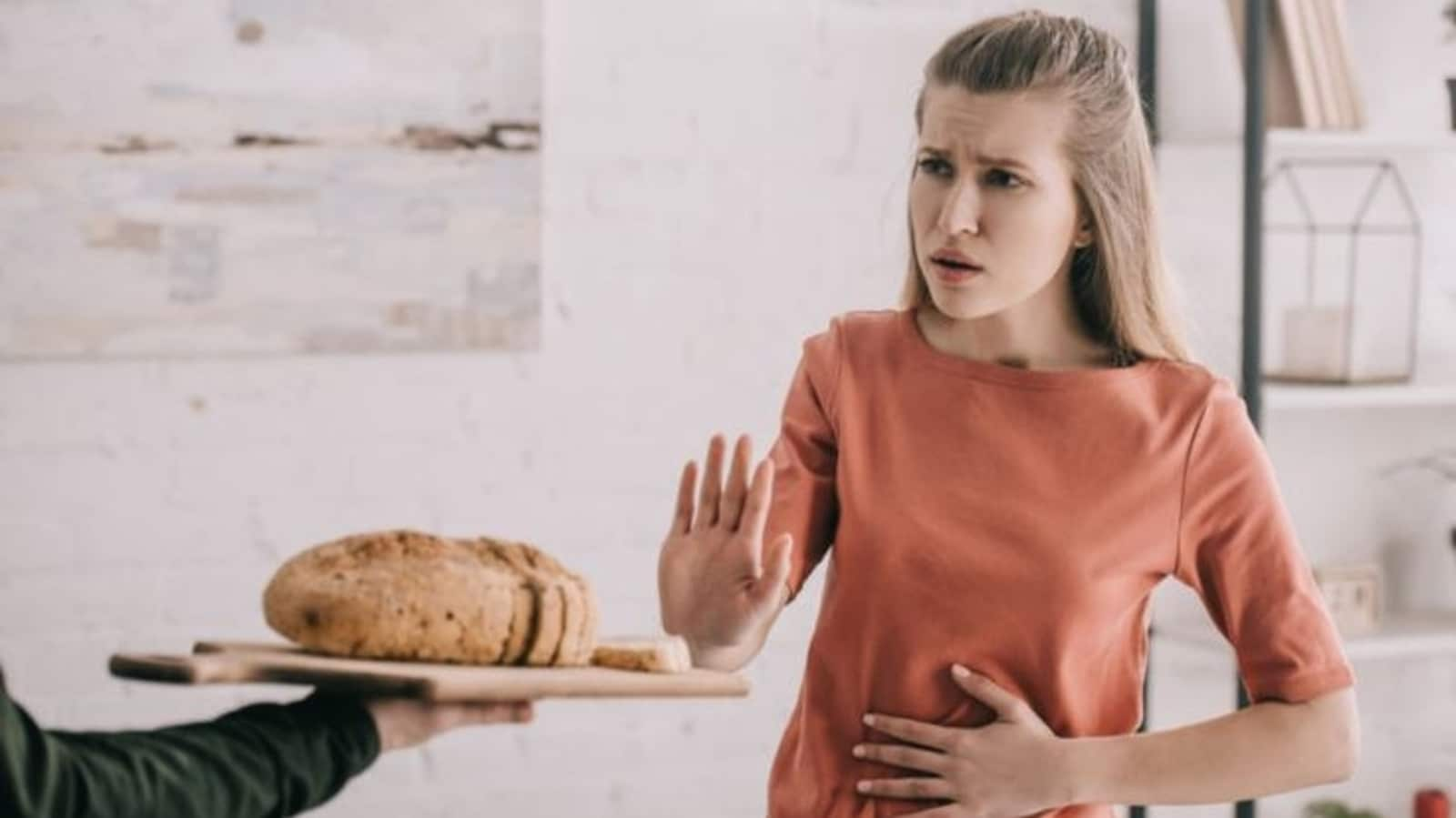
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system responds by damaging the lining of the small intestine, leading to various symptoms and complications.

In an interview with HT Lifestyle, Gurpreet Kaur, Founder of GEGGLE – PrabhGun GlutenFree Organics in Dehradun, explained, “Gluten intolerance or non-celiac gluten sensitivity refers to a condition where individuals experience adverse reactions to gluten consumption but do not have celiac disease or wheat allergy. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and fatigue. For individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, consuming gluten can lead to digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.”
She elaborated, “These symptoms occur due to inflammation and damage to the small intestine. Prolonged exposure to gluten in individuals with celiac disease can impair the absorption of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium and vitamin D. This can result in anemia, osteoporosis, and other complications. Gluten sensitivity can also manifest in non-digestive symptoms, including headaches, joint pain, skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis) and neurological issues such as numbness and tingling in the extremities. These systemic effects highlight the wide-ranging impact of gluten on the body.”
According to her, the primary treatment for celiac disease and gluten intolerance is adopting a strict gluten-free diet. Gurpreet Kaur shared, “This involves avoiding all sources of gluten, including wheat, barley, rye, and their derivatives. Fortunately, there is an increasing availability of gluten-free products and alternatives to support dietary adherence. Individuals with celiac disease and gluten intolerance must become proficient in reading food labels to identify hidden sources of gluten. Look for products labelled as “certified gluten-free,” indicating that they meet strict standards for gluten content.”
Talking about the numerous challenges stemming from widespread unawareness and ignorance surrounding celiac disease and gluten intolerance, she revealed, “These struggles not only affect individuals directly impacted by these conditions but also hinder efforts to provide adequate support and resources for them. One of the primary struggles is the general lack of recognition of celiac disease and gluten intolerance as serious medical conditions. Many people, including healthcare professionals, may dismiss symptoms or attribute them to other causes, delaying diagnosis and treatment. There is a significant amount of misinformation circulating about gluten-related disorders, leading to confusion and skepticism among the public. Misconceptions about the severity of these conditions or the necessity of a gluten-free diet can make it challenging to educate individuals and promote awareness effectively.”
Highlighting that individuals with celiac disease and gluten intolerance often face social stigma and judgment, particularly when adhering to a gluten-free diet in social settings, Gurpreet Kaur said, “Friends, family members and even restaurant staff may not understand the importance of avoiding gluten or may perceive it as a dietary fad rather than a medical necessity. Despite growing demand, access to gluten-free options and certified gluten-free products remains limited in many regions. This lack of accessibility can pose significant challenges for individuals trying to maintain a strict gluten-free diet, especially when dining out or travelling.”
She concluded, “Disparities in healthcare access and knowledge further compound the struggles faced by individuals with celiac disease and gluten intolerance. Limited availability of specialists, inadequate training among healthcare providers, and insurance coverage issues can all impede proper diagnosis and management of these conditions. Living with celiac disease or gluten intolerance can take a toll on individuals’ mental and emotional well-being. Coping with chronic symptoms, dietary restrictions and societal challenges can lead to feelings of isolation, frustration and anxiety. Addressing these struggles requires a multifaceted approach involving education, advocacy and policy changes. By raising awareness about the realities of celiac disease and gluten intolerance, combating misinformation, improving access to gluten-free resources and fostering empathy and support for affected individuals, we can work towards a more inclusive and understanding society.”
[ad_2]
Source link