[ad_1]
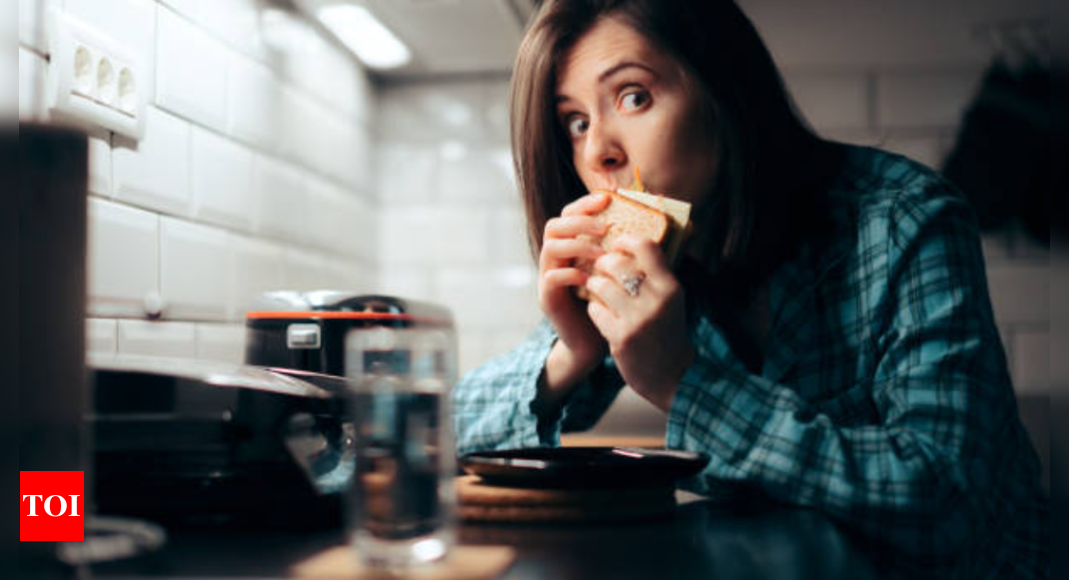
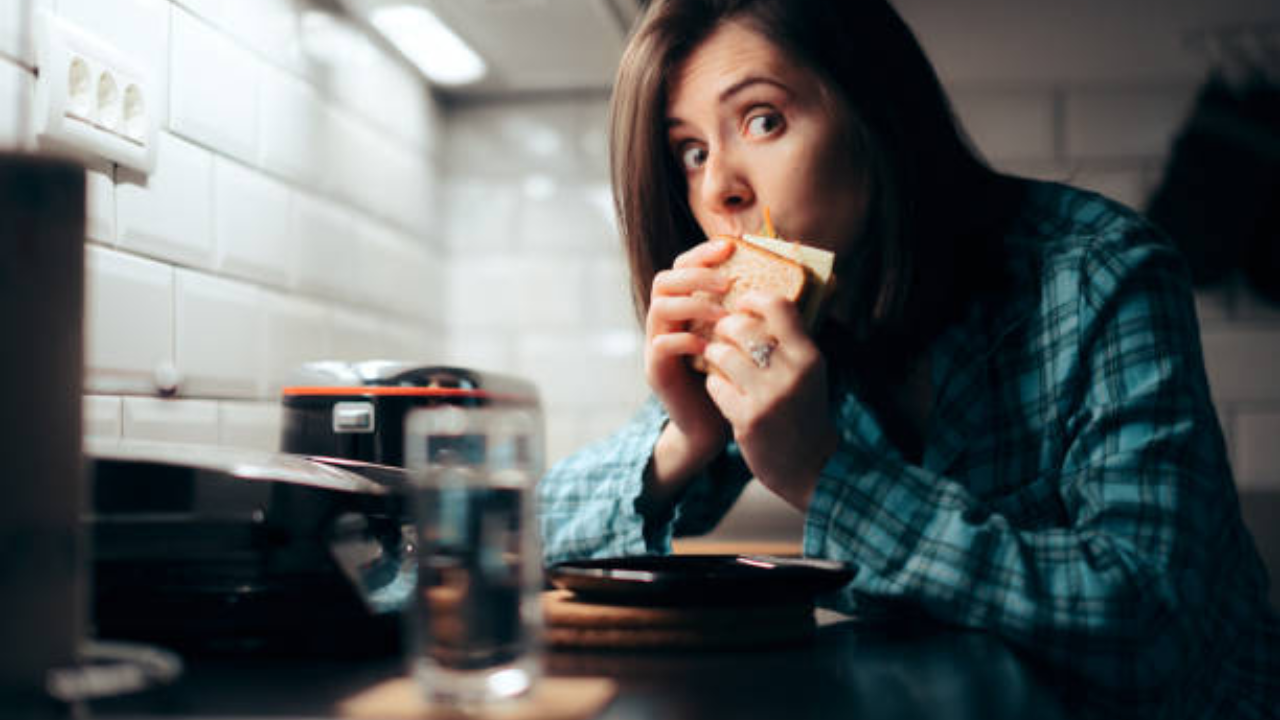
Maybe you didn’t eat sufficiently before going to bed!
One potential reason for waking up hungry at night is an imbalance in your daily eating pattern.If you consume a large meal earlier in the evening and then go to bed several hours later, your body may have processed the food, leaving you feeling hungry again by the time you wake up. Additionally, eating meals that are high in carbohydrates or simple sugars can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to hunger pangs during the night.
Maybe your regular meal is not nutritious enough!
Another factor that may contribute to nighttime hunger is inadequate calorie intake throughout the day. If you’re not consuming enough calories or nutrients during your waking hours, your body may signal hunger during the night as a way to obtain the energy it needs for essential functions and repair processes.
Surprising triggers of winter heart attacks
Other factors that trigger nighttime hunger
Furthermore, certain lifestyle factors, such as stress, anxiety, or physical activity levels, can also influence nighttime hunger. Stress and anxiety can stimulate the release of hormones like cortisol, which can increase appetite and disrupt normal eating patterns. Similarly, engaging in intense physical activity or exercise late in the day may increase your body’s energy requirements and lead to nighttime hunger if not adequately refueled.
What to do to curb nighttime hunger?
Eat a balanced dinner: Opt for a balanced dinner that includes protein, healthy fats, fiber, and complex carbohydrates. This combination can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness, reducing the likelihood of waking up hungry during the night.
Avoid heavy meals before bed: Try to avoid consuming large or heavy meals within a few hours of bedtime. Instead, aim for a lighter meal or snack that won’t overload your digestive system and interfere with sleep.
Include protein and fiber in evening snacks: If you find yourself waking up hungry during the night, consider having a small snack that contains protein and fiber, such as Greek yogurt with fruit, whole grain crackers with cheese, or a handful of nuts. These nutrient-rich snacks can help satisfy hunger and provide sustained energy throughout the night.
Manage stress and anxiety: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle stretching before bedtime to help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Creating a calming bedtime routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Stay hydrated: Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger. Make sure to stay hydrated throughout the day by drinking plenty of water. Keep a glass of water by your bedside in case you wake up feeling thirsty during the night.
Monitor caffeine and alcohol intake: Limit consumption of caffeine and alcohol, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Both substances can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to nighttime hunger.
Establish regular meal and snack times: Try to eat meals and snacks at regular intervals throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent excessive hunger at night. Avoid skipping meals or going long periods without eating, as this can increase the likelihood of nighttime hunger.
Consult a doctor: If you continue to experience persistent nighttime hunger despite implementing these strategies, consider consulting a healthcare professional. They can help identify any underlying medical conditions or dietary factors that may be contributing to your symptoms and provide personalized recommendations for improvement.
[ad_2]
Source link